Have you ever looked up at the stars in the universe and asked, “How does this massive universe operate?” Many people wonder the same thing about the universe. Science gives us amazing answers. We explore the universe’s beginning, structure, and basic rules of the universe.
First, The Big Start: The Big Bang

So, where did it all come from? Well, our universe began with the Big Bang about 13.8 billion years ago. Specifically, it started as an extremely hot, dense point. Then, space itself began expanding rapidly. Immediately, this was not an explosion in space. Instead, it was the growth of space. After this event, the universe cooled down. Next, small particles formed. Finally, these particles created atoms, and then the huge structures we see today. In fact, the universe is still expanding right now!
Next, The Hidden Majority: Dark Matter and Dark Energy
But here is the strangest part. Believe it or not, the stars and planets we see make up less than 5% of everything! The rest is mostly invisible.
- First, there is Dark Matter (about 27%): This stuff does not reflect light. Therefore, we cannot see it. However, we know it exists because of its strong gravity. Actually, Dark Matter acts like a huge, unseen web. It holds galaxies together. Otherwise, the galaxies would just fly apart.
- Second, we find Dark Energy (about 68%): This is even more mysterious. Crucially, Dark Energy makes the universe’s expansion speed up. Think of it as an anti-gravity force on the largest scale. Currently, understanding Dark Energy is a major science goal.
Then, The Governing Rules: Four Forces of Universe
Indeed, four basic forces control everything that happens in space.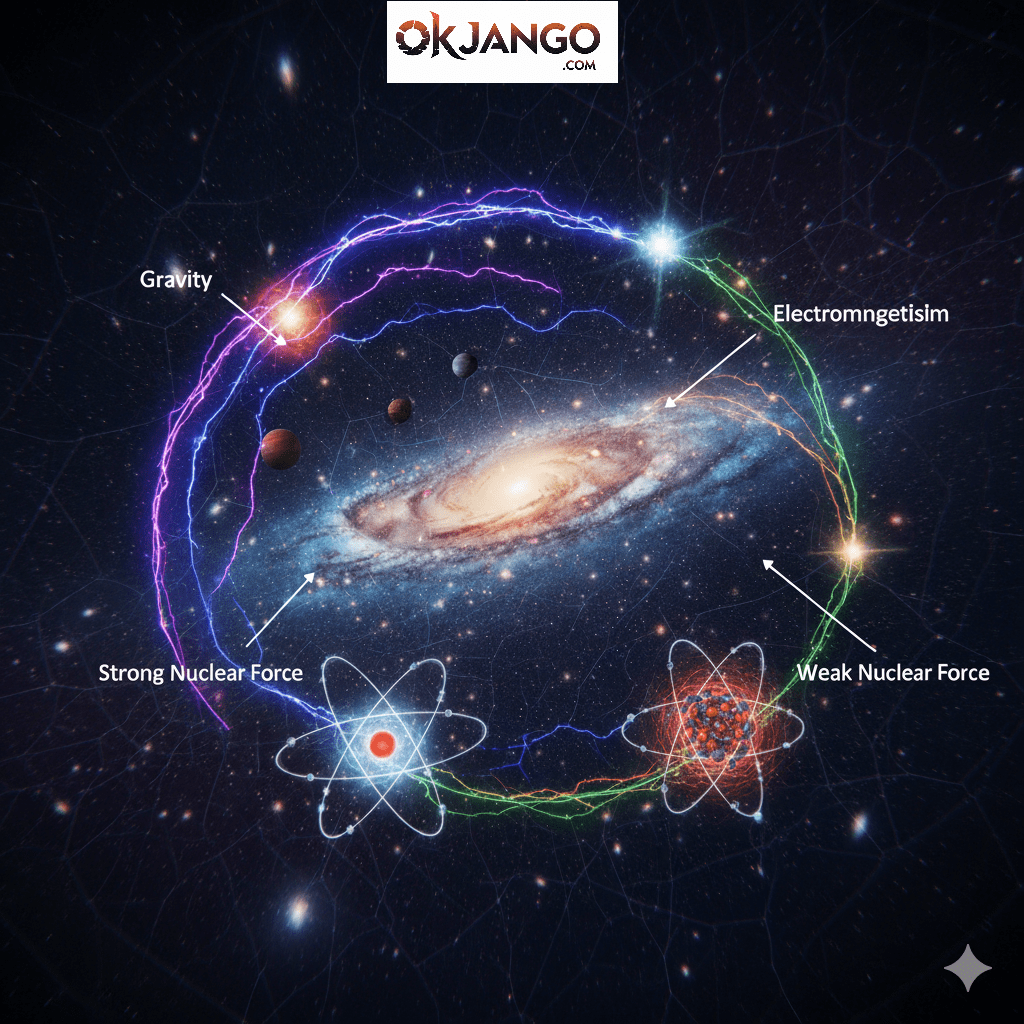
- Gravity: This is the pull between objects with mass. It dominates the cosmos. Consequently, it shapes planets, stars, and galaxies.
- Electromagnetism: This force controls charged particles. It binds atoms into molecules. Moreover, it creates light.
- Strong Nuclear Force: This is the most powerful force. It glues protons and neutrons inside atoms.
- Weak Nuclear Force: Finally, this force causes atomic decay. It powers the sun’s nuclear reactions.
Finally, The Structure: From Small to Huge
Over time, gravity created the universe’s stunning structure. Initially, tiny particles became atoms. Subsequently, atoms formed massive clouds. These collapsed to ignite stars. Then, stars grouped into enormous galaxies. Furthermore, galaxies collect into large clusters and huge superclusters. Ultimately, these groups form a “cosmic web” with massive empty spaces called voids.
The universe is an incredible, ongoing story. Thus, every discovery makes us appreciate its beauty more. Truly, we live in an exciting age of science. Therefore, next time you see the stars, remember you look at billions of years of cosmic history!
Further Reading and References about Universe
For those who wish to delve deeper into the mechanics and mysteries of the universe, here are some reliable sources and organizations dedicated to cosmology and astrophysics:
- NASA’s Official Cosmology Page: Provides accessible information and the latest news on missions, projects, and discoveries related to the Big Bang, Dark Energy, and the structure of the cosmos.
- European Space Agency (ESA) Science & Exploration: Features detailed articles and mission results (like Planck and Gaia) that contribute to our understanding of the universe’s composition and expansion.
- Symmetry Magazine (Fermilab & SLAC): Focuses on particle physics and its intersection with cosmology, offering well-explained articles on Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and fundamental forces.
- The Big Bang Theory (CERN): A brief, authoritative overview of the Big Bang model, explained by the European Organization for Nuclear Research.
- HubbleSite (STScI): Provides stunning images and scientific summaries from the Hubble Space Telescope, illustrating the structure and evolution of galaxies.
- HubbleSite
Read more blogs at : Okjango.com
- HubbleSite


